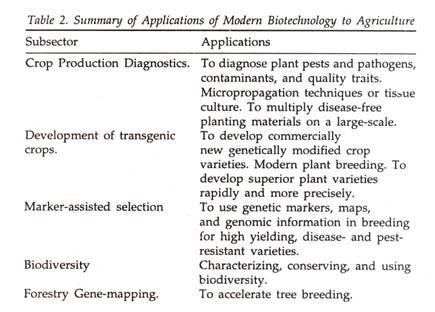
Here is a term paper on ‘Biomolecules’ for class 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short term papers on ‘Biomolecules’ especially written for school and college students.
Term Paper on Biomolecules
Term Paper Contents:
- Term Paper on the Definition of Biomolecules
- Term Paper on the Functions of Different Biomolecules
- Term Paper on the Characteristics of Biomolecules
- Term Paper on the Chemical Bonds in Biomolecules
Term Paper # 1. Definition of Biomolecules:
Plants and animals are made up of many chemical substances. There are certain complex organic molecules which form the basis of life. These build up living organisms are also required for the growth and maintenance of plants and animals.
The chemical composition and the metabolic reactions of these living organisms appear to be similar in many ways. The composition of living tissues and non-living matter also appear to be similar in qualitative analysis. A closer analysis reveals that the relative abundance of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is higher in the living system.
Such molecules are called Biomolecules. The main classes of biomolecules are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, enzymes, and hormones. All forms of life are composed of biomolecules only and this is due to the fact that all living organisms are made up of cells which has a number of biomolecules in it.
A biomolecule is any molecule that is produced by a living organism, including large macromolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, lipids and nucleic acids as well as small molecules such as primary metabolites, secondary metabolites, and natural products.
There are number of molecules in a cell which is known as cellular pool. The cellular pool has water, inorganic and organic molecules serving as raw materials for biochemical reactions. The cell as a whole contains both micro-molecules and macromolecules which are compatible with life because of their special properties.
Term Paper # 2. Functions of Different Biomolecules:
There are several types of biomolecules. The most importance biomolecules are the nucleotides that make up DNA and RNA which carries the genetic information and are important in heredity.
There are also the lipids which function as the building blocks of biological membranes and as energy providing molecules. The hormones serve in the regulation of metabolic processes. The carbohydrates are also important in the provision of energy and serves as energy storage molecules.
Amino acids and proteins have major function in living organisms which includes synthesis of proteins, formation of genetic code, and works as biomolecules that assist in other processes such as lipid transport. Vitamins are also necessary for the survival and health of organisms. Though vitamins are not synthesized by organisms, these are important biomolecules.
Term Paper # 3. Characteristics of Biomolecules:
i. Most of the biomolecules are organic compounds.
ii. They have specific shapes and dimensions.
iii. A functional group determines the chemical properties of biomolecules.
iv. Macromolecules are large molecules and are constructed from small building block molecules.
Term Paper # 4. Chemical Bonds in Biomolecules:
The essence of biological processes is the basis of the uniformity in their living ways. It is in its most fundamental sense the molecular interactions i.e. chemistry among molecules.
Biochemistry is chemistry that deals with the chemical process in living systems. To understand this, we will study chemical bonding. The strongest bonds that are present in biochemical are covalent bonds, which hold atoms together within molecules. A covalent bond is formed by sharing of a pair of electrons between adjacent atoms.
For example, C-C bond has bond length of 1.54 Å and bond energy of 85 k cal/mol. As the energy is relatively high, more energy is required to break it. More than one electron needs to be shared between 2 atoms to form multiple covalent bond.
Non covalent molecules interactions are required in replication of DNA, folding of proteins, and detection of molecular signals.
There are three fundamental non-covalent bonds:
i. Electrostatic interactions,
ii. Hydrogen bonds and
iii. Van der waals interactions.
i. Electrostatic interactions:
An electrostatic interaction depends on the electric charges on atoms.
ii. Hydrogen bond:
These are weak interactions present in DNA by proteins. H atom is shared between H bond is partly shared between two electronegative atoms. H bonds are electrostatic interactions and are weaker than covalent bonds.
iii. Van der waals interactions:
Distribution of electronic charge around an atom changes with live and is not symmetric. The attraction between atoms increases as they come closer to each other until they are far away from each other. When atoms are closer, Van der waals forces are very strong. Energies associated with van der waals interactions are quite small.