In this article we will discuss about the principle, requirements and procedure for Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP) analysis.
Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism is a nucleic acid finger printing method to find out genetic variation that exists between closely related genes. This method was designed by Zabeau and Vos (1993) and Vos et al. (1995). AFLP is used for the analysis of plant and animal genetic mapping, medical diagnostics, phylogenetic studies and microbial typing.
This method is based on PCR amplification and is a time saving alternative for generating large numbers of polymorphic bands (AFLP markers) on polyacrylamide gels. There are several advantages for AFLP over other DNA markers. The most important ones are their capacity to inspect the entire genome for polymorphism and its reproducibility.
Principle:
From a digest of total genomic DNA, selective amplification of restriction fragments is made using PCR. It is a dominant marker. With AFLP, molecular genetic polymorphisms are identified by the presence or absence of DNA fragments following restriction and amplification of genomic DNA.
The process consists of four steps:
(i) Digestion of genomic DNA
(ii) Ligation of adapters
(iii) PCR amplification and
(iv) Gel analysis.
Requirements:
Reagents:
Digestion/Ligation Buffer:
1. Tris HCl (pH 7.5): 50.0 mM
Mg-acetate: 50.0 mM
K-acetate: 250.0 mM
Bovine serum albumin: 25.0 ng/µl
2. Adopter preparation buffer
Tris HCl (pH 7.5): 100 mM
Mg acetate: 100 mM
K-acetate: 500 mM
ATP: 10 mM
3. Restriction Enzymes-£co-RI and Mse-l.
4. T4 DNA Lygase.
5. Adapter oligonucleotides.
Eco-Rl adapter 1
5’CTCGTAGACTGCCTACC
Eco-Rl adapter 2
5′ AATTGGTACGCAGTC
Mse-l adapter 1
5’GACGATGAGTCCTGAG
Mse-l adapter 2
5’ TACTCAGGACTCAT
6. PCR buffer (10x)
Tris HCl (pH 9.0): 100 mM
KCl: 500 mM
7. Tris buffer (pH 7.5)
dNTP mix 5mM
(γ33P) ATP • 3000 Ci/mmol
Taq DNA polymerase 5 U/µl
8. T4 polynucleotide kinase
Eco-RI core + adapt primer
5 ‘ CTCGTAGACTGCGTACCAATTC
Mse-l core + adapt primer
5′ GACGATGAGTCCTGAGTAA
Ero-RI AFLP primers
5 AGACTGCGTACCAATTC xyz
MSE. I-AFLP primers
5′ GATGAGTCCTGAGTAA xyz
9. Formamide buffer (2x):
Formamide: (V/V) 98%
EDTA (pH 8.0) : 10mM
Xylene cyanol F.F (W/V) 0.025%
Bromophenol blue (W/V): 0.025%
10. TBE buffer (5x):
Tris Borate -450 mM
EDTA (pH 8.0) -10 mM
Acrylamide/bisacrylamide stock 19.1 with urea.
11. Microcentrifuge and PCR tubes.
12. Micropipettes and tips.
13. Water bath.
14. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic aparatus/sequencing gel apparatus.
15. PAGE reagents.
16. Film cassette.
17. X-ray film.
Reagents for developing and fixing auto radiograms.
Procedure:
i. Isolation and Restriction Digestion of Genomic DNA:
1. DNA should be isolated from plant parts (leaf/stem) and stored at-80°C till DNA extraction.
2. For one sample DNA mix the following:
DNA: 0.5 µg
Digestion/Ligation buffer: 8.0 µl
Eco-Rl and Mse-l each: 1.0 µl
Distilled water to make up 40.0 µl
3. Mix gently and briefly centrifuge and incubate at 37°C for 2 hours.
4. To inactivate restriction endonucleases incubate the mixture at 70°C for 15-20 minutes.
5. Keep the tubes on ice, briefly centrifuge and collect the contents.
ii. Ligation of Adapters:
6. Mix the following for preparation of Eco-RI and Mse-I specific as adapter:
7. In these mixtures the final Eco-RI and Mse-I specific ds adapter concentrations are 5 and 50 p-mol/ml respectively. Adapters should not be phosphorylated in order to prevent its self-ligation. Adapter mixtures should be heated to 95°C and slowly allowed to cool to room temperature. These ds adapters are enough for 60 reactions.
Mix the following to each 40 ml of digested DNA:
8. Incubate ligation reactions at room temperature for 2 hours. Adapters are irreversibly ligated to template DNAs because of a single-bp change at the R.E. site.
iii. Amplification by PCR:
The x, y and z on the AFLP primers are the extensions of the 3 end. This can vary in length and sequence between primers.
Preamplification Mixture:
Mix gently and centrifuge briefly.
“Core + adapt primer”- primers are homologous to the RE recognition site and adapter sequences only. This promotes amplification beyond restriction site.
Amplify the reactions with the following heat cycles:
9. Dilute preamplification products to 1:10 with T.E. buffer and store at -20°C until required.
Primer labeling:
Eco-RI-AFLP primers are end labelled with ϒ33P ATP/ϒ32P ATP in the following mixture:
Gently mix and centrifuge, collect contents of tube and incubate reaction mixture at 37°C for one hour. This stimulates kinase activity. Now heat at 70°C for 10 minutes to inactivate enzyme activity. The final concentration of primers will be 10 ng/µl.
Selective amplification/AFLP PCR:
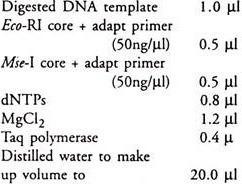
Set up each AFLP-PCR by combining 1ml diluted preamplified template DNA with:
Mix gently, centrifuge briefly.
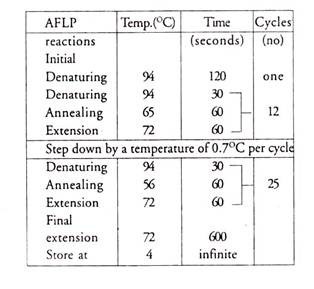
Amplify AFLP reactions with a step down PCR profile:
iv. Separation by gel and analysis:
1. To each AFLP-PCR product add equal volume of 2x formamide buffer and incubate at 95°C for three minutes. This denatures DNA. Immediately cool it on ice and load the denatured samples on 5% polyacrylamide gel (with 7.5 M urea + 1x TBE)
2. Electrophorise at constant current (60W) with 0.5x TBE as buffer used for running and stop when xylene cyanol dye front is 1—2 cm from the bottom of the gel.
3. Blot gel with filter paper with vacuum heat gel drier. Generate autoradiograph of labelled DNA finger prints.