In this article we will discuss about the principle, requirements and procedure for isolation of blue green algae.
Blue green algae (BGA), the Cyanobacteria, occur in wet land cultivations of rice. They are free-living N2 fixers and are photosynthetic organisms. Species of Nostoc, Anabaena, Scytonema, Calothrix, etc. are a few among the many BGA that fix nitrogen. Most of the forms have a mucilaginous covering which inhabit bacteria.
Principle:
Since they are autotrophic and nitrogen fixers, they can be isolated on a N2 free inorganic medium.
Requirements:
1. BGA containing soil samples from rice fields.
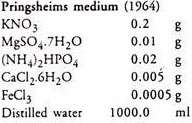
2. Inorganic medium:
3. Sterile water blanks (99 ml and 9 ml).
4. Sterile pipettes.
5. Several sterile flasks/ bottles with inorganic medium.
6. Illuminated growth room.
7. Bunsen burner/laminar clean air flow hood.
Procedure:
1. Prepare dilutions of weighed samples of BGA in the water blanks as given in dilution plate method given for bacteria.
2. Inoculate each aliquot into the several flasks / bottles with sterile inorganic medium.
3. Label and incubate for several weeks in an illuminated room at 28° – 30°C.
4. Pick up individual colonies and transfer them to fresh media for growth and identification.