The following points highlight the top twelve techniques used for screening of libraries. Some of the techniques are: 1. Hybridization Probing 2. Chromosome Walking 3. PCR Screening 4. Fluorescence Insitu Hybridization (FISH) 5. Molecular Beacons 6. Gene Tagging 7. Screening Based on in Vitro Translation of mRNA 8. Immunological Screening and Others.
Screening of Library: Technique # 1.
Hybridization Probing:
This is the screening of a library with a labelled probe (radioactive, bioluminescent, etc.) to identify a specific sequence of DNA or RNA. This can be either colony hybridization probing, in which we search for a specific DNA sequence in a mixed population of transformed bacterial host cells, or plaque hybridization in which we screen bacteriophage plaques.
Screening of Library: Technique # 2.
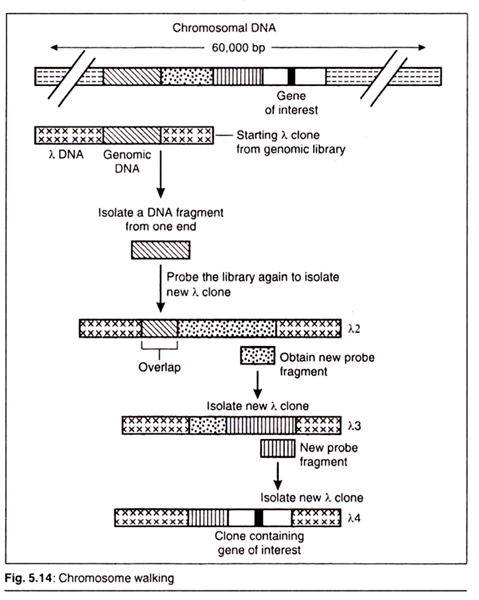
Chromosome Walking:
Chromosome walking utilizes overlapping fragments of a particular chromosome to isolate gene of interest which may be present upstream and downstream from the original DNA fragment (Fig.5.14).
Screening of Library: Technique # 3.
PCR Screening:
The combinatorial screening carried out by PCR is the most sensitive and one of the fastest ways available for the screening of DNA libraries (Fig. 5.15).
Screening of Library: Technique # 4.
Fluorescence Insitu Hybridization (FISH):
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a cytogenetic technique developed that is used to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. This technique can also be successfully used to detect our gene of interest within the mixture various recombinant clones (Fig. 5.16).
Screening of Library: Technique # 5.
Molecular Beacons:
A molecular beacon is a fluorescent probe molecule that is designed to fluoresce only when it binds to a specific DNA target sequence (Fig. 5.17).
Screening of Library: Technique # 6.
Gene Tagging:
This method is used only when we do not have any information regarding the base sequence of our gene of interest but can detect a specific phenotype encoded by it. This method rely on integration of known sequence of DNA, known as tags, preferably at random sites in the genome of the host cell.
Screening of Library: Technique # 7.
Screening Based on in Vitro Translation of mRNA:
If the desired sequence codes for a protein, and the protein has been characterized, then it is possible to identify the protein product by two methods based on translation of mRNA in vitro. There two types of method in this regard – Hybrid-arrest translation (HART) and Hybrid-release translation (HRT).
Screening of Library: Technique # 8.
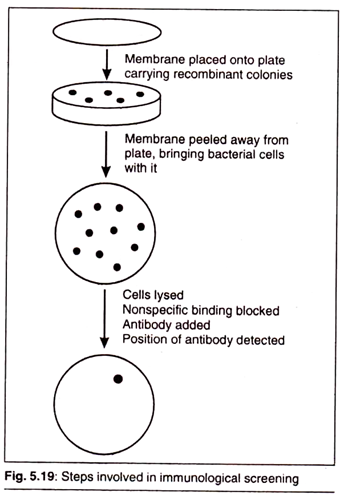
Immunological Screening:
This method aims at identifying the protein product of a cloned gene. The technique requires that the protein is expressed in recombinants. In this method, instead of a nucleic acid probe, a specific antibody is used (Fig 5.19).
Screening of Library: Technique # 9.
Fluorescent-Activated Cell Sorter (FACs):
The fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACs) is a machine that can rapidly separate the cells in a suspension on the basis of presence or absence of fluorescence. FACs is used to screen those gene of interest whose protein products are expressed on the surface of the cell (Fig. 5.21).
Screening of Library: Technique # 10.
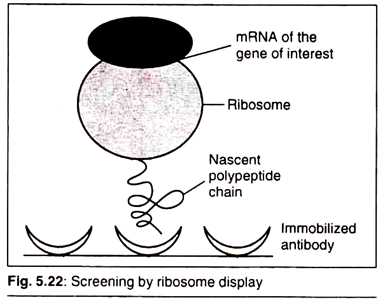
Ribosome Display:
In this process the gene of interest is allowed to express in vitro. A pool of ribosomes that are in the process of translation (and thus contain mRNA and the corresponding nascent peptides of our gene of interest) is passed over the solid phase with corresponding antibody attached to it (Fig. 5.22).
Screening of Library: Technique # 11.
South-Western Screening:
This method of screening is used when the gene of interest encodes for a sequence specific DNA binding protein.
Screening of Library: Technique # 12.
North-Western Blotting:
This method of screening is used when the gene of interest encodes for a sequence specific RNA binding protein.